When it comes to creating a perfect seal in industrial and everyday applications, gaskets are the unsung heroes. But did you know there’s a whole science behind selecting the right gasket? Choosing the wrong one can lead to leaks, system failures, or costly repairs. So, what’s the deal with metallic and non-metallic gaskets? Let’s break it down.
What Are Gaskets?
Gaskets are essential sealing components that fill gaps between two mating surfaces, preventing leaks and maintaining system integrity. Think of them as the glue that keeps everything airtight and watertight without actually being glue.
Primary Functions of Gaskets
Ensuring a Leak-Proof Seal
The main job of a gasket is to stop fluids, gases, or solids from escaping. It’s like a protective wall for your system.
Resistance to Pressure and Temperature
A good gasket can handle the heat and pressure, literally! It ensures your systems work smoothly under varying conditions.
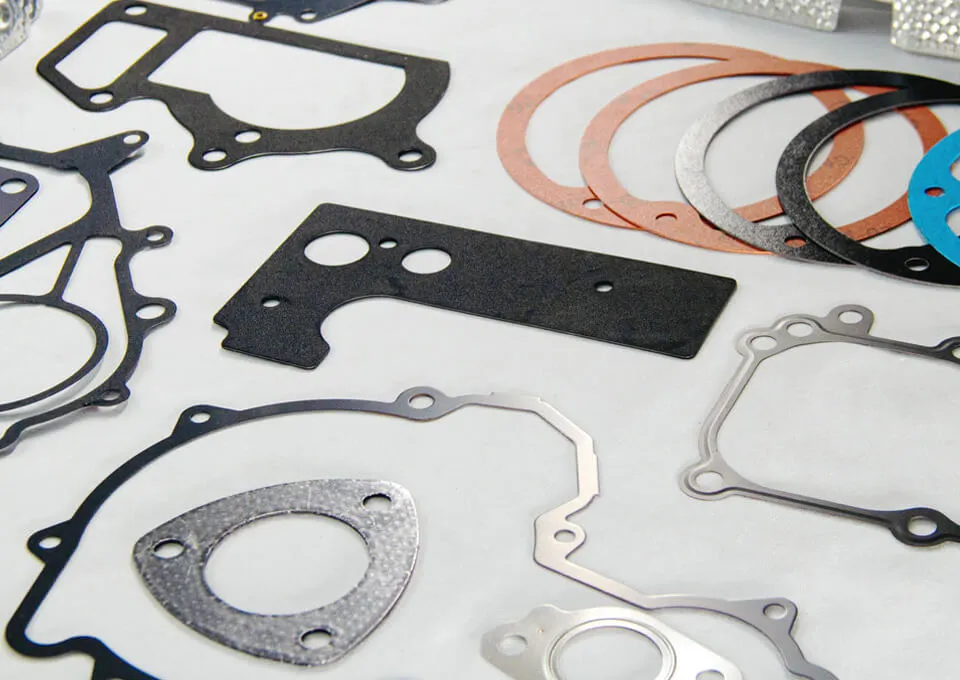

Definition of Metallic Gaskets
Metallic gaskets are made entirely of metal or a combination of metals. They are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Common Materials Used
Stainless Steel
Known for its strength and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel is a top choice.
Monel and Other Alloys
Special alloys like Monel offer exceptional resistance to chemicals and extreme conditions.
Key Features of Metallic Gaskets
High durability
Resistance to extreme temperatures
Perfect for industrial settings
Definition of Non-Metallic Gaskets
Non-metallic gasket materials are made from soft, pliable materials like rubber, graphite, or PTFE, making them ideal for low-pressure applications.
Common Materials Used
Rubber
Flexible and cost-effective, rubber gaskets are popular for everyday uses.
PTFE (Teflon)
Known for its non-stick properties, PTFE handles chemicals like a pro.
Graphite
Perfect for high-temperature applications, graphite is a versatile non-metallic option.
Key Features of Non-Metallic Gaskets
Flexibility and adaptability
Chemical resistance
Cost-effective for many applications

Material Composition
Metallic gaskets are rigid and durable, while non-metallic ones are soft and flexible.
Performance in High-Pressure Environments
Metallic gaskets excel in high-pressure scenarios, whereas non-metallic gaskets work better in low-pressure setups.
Temperature Resistance
Metallic gaskets can handle extreme heat, but non-metallic gaskets have limitations depending on the material.
Cost and Maintenance
Non-metallic gaskets are generally more affordable and easier to replace.
Advantages
Excellent for high-pressure systems
Resistant to extreme conditions
Limitations
Expensive and harder to install
Not suitable for low-pressure uses
Advantages
Flexible and easy to install
Cost-effective for most applications
Limitations
Limited temperature and pressure resistance
May degrade over time in harsh environments
Industrial Uses
Oil and Gas Industry
Metallic gaskets are the backbone of pipelines and refineries.
Chemical Processing Plants
They ensure leak-proof operations in chemical-heavy environments.
Everyday Uses
Plumbing Systems
Non-metallic gaskets keep your plumbing leak-free.
Food and Pharmaceutical Industries
They provide safe sealing solutions where hygiene is crucial.
Factors to Consider
Pressure and Temperature Requirements
Understand the operating conditions to pick the right type.
Compatibility with Medium
Choose a material that won’t react with the substance being sealed.
Budget Considerations
Don’t break the bank if a non-metallic option will do the job.
Importance of Consulting Experts
When in doubt, ask an expert. It’s better than a costly mistake!
Gaskets might seem small, but they’re the guardians of system integrity. Metallic gaskets shine in extreme conditions, while non-metallic ones are versatile and budget-friendly. The choice ultimately depends on your needs, but understanding the differences helps you make the right call.